Table of Contents
- What is a Bill of Materials (BOM)?
- Importance of a Bill of Materials
- Types of Bill of Materials
- Engineering BOM (EBOM)
- Manufacturing BOM (MBOM)
- Sales BOM (SBOM)
- Service BOM
- Elements of a Bill of Materials
- Creating a Bill of Materials
- Example of a Bill of Materials
- BOM Example for Download
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Conclusion
What is a Bill of Materials (BOM)?
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a detailed list of all the components, parts, and materials required to manufacture a product. It includes the part numbers, descriptions, quantities, and sometimes the suppliers of each item. The BOM is an essential document used in the manufacturing process to ensure that all necessary components are accounted for and procured in the correct amounts.
The BOM is often hierarchical, with the top level representing the finished product and the lower levels representing the subassemblies and individual components. This hierarchical structure allows for a clear understanding of how the product is assembled and helps in identifying the relationships between the various components.
Importance of a Bill of Materials
The Bill of Materials is a critical document in the manufacturing process for several reasons:
-
Ensures accurate production: By providing a detailed list of all required components and their quantities, the BOM helps ensure that the manufacturing process runs smoothly and that the final product is assembled correctly.
-
Facilitates procurement: The BOM serves as a guide for the procurement team, allowing them to order the necessary components in the correct quantities and from the appropriate suppliers.
-
Helps in cost estimation: By listing all the required components and their quantities, the BOM enables accurate cost estimation for the product, taking into account the cost of each component and the total number of units to be produced.
-
Assists in inventory management: The BOM helps in planning and managing inventory levels by providing information on the required quantities of each component, allowing for optimal stock levels and minimizing the risk of stockouts or overstocking.
-
Supports product revisions: As products undergo revisions or updates, the BOM is updated accordingly, ensuring that the changes are reflected in the manufacturing process and that the correct components are used.

Types of Bill of Materials
There are several types of BOMs, each serving a specific purpose in the product development and manufacturing process. Let’s take a look at the most common types:
Engineering BOM (EBOM)
The Engineering BOM (EBOM) is created by the design team and contains all the components and parts required to build a product as designed. It includes all the necessary technical specifications, such as dimensions, materials, and tolerances. The EBOM is typically created using computer-aided design (CAD) software and serves as the basis for the Manufacturing BOM.
Manufacturing BOM (MBOM)
The Manufacturing BOM (MBOM) is derived from the EBOM and is tailored to the specific needs of the manufacturing process. It takes into account any changes or optimizations made for manufacturability, such as substituting components or altering the assembly sequence. The MBOM is used by the production team to guide the actual manufacturing process.
Sales BOM (SBOM)
The Sales BOM (SBOM) is a simplified version of the BOM, used by the sales team to communicate the product structure to customers. It typically includes only the top-level components or modules and may omit detailed information about individual parts or subassemblies.
Service BOM
The Service BOM is used by the service and maintenance teams and includes all the components and parts required for servicing or repairing a product. It may include additional items such as consumables, spare parts, and tools necessary for maintenance tasks.
Elements of a Bill of Materials
A typical BOM includes the following elements:
- Part number: A unique identifier for each component or assembly.
- Part name or description: A brief description of the part or component.
- Quantity: The number of units of each component required to manufacture one unit of the finished product.
- Unit of measure: The standard unit used to measure the quantity of each component (e.g., pieces, liters, kilograms).
- Procurement type: Indicates whether the component is manufactured in-house, purchased from an external supplier, or a subassembly.
- Reference designators: Used to identify the specific instances of a component in the product, particularly in the case of electronic assemblies.
- Notes or comments: Additional information about the component, such as its purpose, specific requirements, or handling instructions.
Here’s an example table illustrating the elements of a BOM:
| Part Number | Description | Quantity | Unit of Measure | Procurement Type | Reference Designator | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | Motherboard | 1 | pcs | Purchased | MB1 | Rev 2.1 |
| 1002 | CPU | 1 | pcs | Purchased | CPU1 | 3.2 GHz |
| 1003 | RAM | 2 | pcs | Purchased | RAM1, RAM2 | 8 GB DDR4 |
Creating a Bill of Materials
Creating a BOM involves several steps and requires input from various teams, including design, engineering, and procurement. The general process for creating a BOM is as follows:
-
Design the product: The design team creates the initial product design using CAD software, specifying the components, materials, and dimensions.
-
Create the EBOM: Based on the product design, the engineering team creates the EBOM, listing all the required components and their specifications.
-
Review and optimize: The EBOM is reviewed by the manufacturing and procurement teams to identify any potential issues or opportunities for optimization. Changes may be made to improve manufacturability or reduce costs.
-
Create the MBOM: Once the EBOM is finalized, the manufacturing team creates the MBOM, incorporating any changes or optimizations necessary for the production process.
-
Assign part numbers: Each component in the BOM is assigned a unique part number for easy identification and tracking.
-
Add quantities and procurement information: The quantity of each component required for one unit of the finished product is added to the BOM, along with information on how each component will be procured (e.g., in-house, external supplier).
-
Review and approve: The completed BOM is reviewed and approved by all relevant stakeholders, including design, engineering, manufacturing, and procurement teams.
Example of a Bill of Materials
Here’s an example of a simplified BOM for a desktop computer:
| Level | Part Number | Description | Quantity | Unit of Measure | Procurement Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1000 | Desktop Computer | 1 | pcs | Manufactured |
| 1 | 1001 | Motherboard | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1002 | CPU | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1003 | RAM | 2 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1004 | HDD | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1005 | Power Supply | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1006 | Case | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1007 | Keyboard | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
| 1 | 1008 | Mouse | 1 | pcs | Purchased |
In this example, the Desktop Computer (part number 1000) is the top-level item, and it consists of several components, such as the Motherboard (1001), CPU (1002), RAM (1003), and so on. The quantity column indicates the number of each component required to assemble one Desktop Computer.
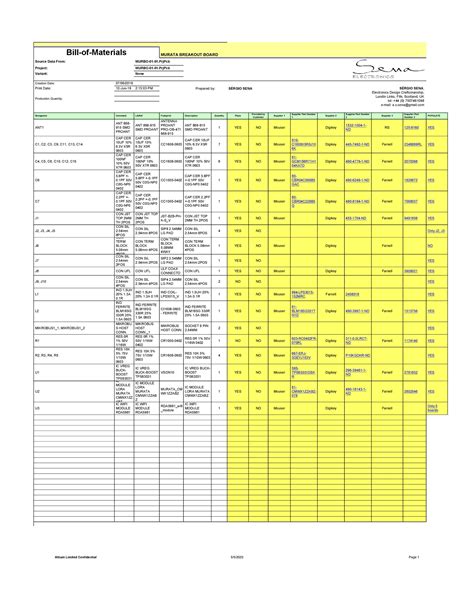
BOM Example for Download
To provide a more detailed example of a BOM, we have created a sample BOM for a wireless bluetooth speaker, which you can download in Excel format: Wireless Bluetooth Speaker BOM
This example includes multiple levels of assemblies and subassemblies, demonstrating the hierarchical structure of a BOM. It also includes additional information such as part descriptions, quantities, units of measure, procurement types, and reference designators.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is the difference between an EBOM and an MBOM?
-
An Engineering BOM (EBOM) is created by the design team and includes all the components and parts required to build a product as designed. A Manufacturing BOM (MBOM) is derived from the EBOM and is tailored to the specific needs of the manufacturing process, taking into account any changes or optimizations made for manufacturability.
-
What is a single-level BOM?
-
A single-level BOM lists all the components and parts required to build a product, but it does not show the hierarchical relationships between the components. In other words, it does not indicate which components are subassemblies or part of other assemblies.
-
What is a multi-level BOM?
-
A multi-level BOM, also known as an indented BOM, shows the hierarchical relationships between the components and subassemblies of a product. It lists the components in a tree-like structure, with the finished product at the top level and the individual components and subassemblies at lower levels.
-
What is the purpose of a BOM in inventory management?
-
A BOM helps in planning and managing inventory levels by providing information on the required quantities of each component, allowing for optimal stock levels and minimizing the risk of stockouts or overstocking. It enables the procurement team to order the necessary components in the correct quantities and at the right time.
-
Can a BOM be used for cost estimation?
- Yes, a BOM can be used for cost estimation. By listing all the required components and their quantities, a BOM enables accurate cost estimation for a product, taking into account the cost of each component and the total number of units to be produced. This information can be used to determine the overall cost of the product and to make pricing decisions.
Conclusion
A Bill of Materials (BOM) is a critical document in the manufacturing process, providing a comprehensive list of all the components, parts, and materials required to produce a product. It serves as a central reference for design, engineering, procurement, and manufacturing teams, ensuring that all necessary components are accounted for and procured in the correct quantities.
By understanding the different types of BOMs, their elements, and the process of creating a BOM, manufacturers can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and reduce the risk of errors or delays in the production process. Implementing a well-structured BOM can lead to significant benefits, such as improved inventory management, accurate cost estimation, and smoother product revisions.
In this article, we have provided a detailed overview of BOMs, their importance, types, and elements, along with an example BOM for download. We hope that this information will be valuable for manufacturers, engineers, and anyone involved in the product development and manufacturing process.





Leave a Reply