PCB Blog
-
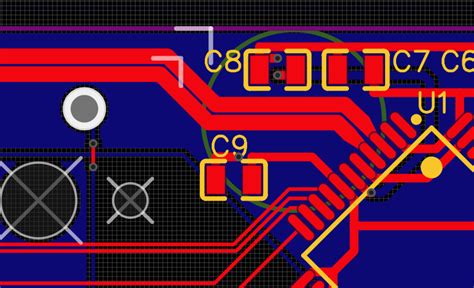
 Read more: Introduction to PCB design of impedance matching with zero resistance
Read more: Introduction to PCB design of impedance matching with zero resistanceWhat is PCB impedance matching? PCB impedance matching is a crucial aspect of designing printed circuit boards (PCBs) to ensure optimal signal integrity and minimize signal reflections. It involves matching the impedance of the transmission lines on the PCB to the impedance of the source and load components. When the […]
-
How to Design PCB Stackup
Posted by
–
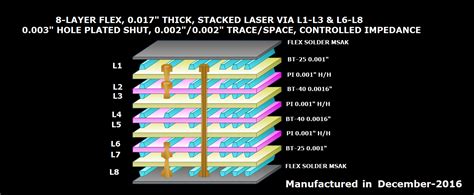 Read more: How to Design PCB Stackup
Read more: How to Design PCB StackupWhat is PCB Stackup? PCB stackup refers to the arrangement of copper and insulating layers in a printed circuit board (PCB). It is a critical aspect of PCB Design, as it determines the board’s electrical properties, mechanical strength, and manufacturability. A well-designed PCB stackup ensures proper signal integrity, reduces electromagnetic […]
-
DDR2 800 for PCB signal integrity design and DDR
Posted by
–
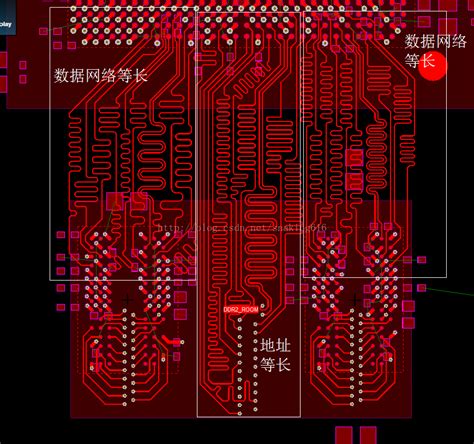 Read more: DDR2 800 for PCB signal integrity design and DDR
Read more: DDR2 800 for PCB signal integrity design and DDRKey Characteristics of DDR2 800 DDR2 800 SDRAM has the following key characteristics: Operates at a clock frequency of 400 MHz with data transfers on both edges of the clock signal, providing an effective data rate of 800 MT/s (mega transfers per second) Uses SSTL_18 (Stub Series Terminated Logic for […]
-
PCB Stackup Planning Simple
Posted by
–
 Read more: PCB Stackup Planning Simple
Read more: PCB Stackup Planning SimpleIntroduction to PCB Stackup Printed Circuit Board (PCB) stackup is a crucial aspect of PCB design that determines the arrangement of copper layers and insulating materials within a PCB. It plays a significant role in the overall performance, reliability, and manufacturability of the final product. In this comprehensive guide, we […]
-
RAYPCB Plugin for KiCad Available Now
Posted by
–
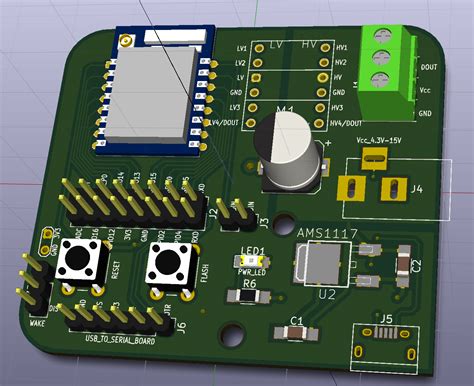 Read more: RAYPCB Plugin for KiCad Available Now
Read more: RAYPCB Plugin for KiCad Available NowWhat is RAYPCB? RAYPCB is a powerful new plugin for KiCad, the popular Open-source PCB design software. This plugin integrates RAYPCB’s advanced PCB manufacturing capabilities directly into the KiCad interface, making it easier than ever to design and manufacture high-quality printed circuit boards. Some of the key features of RAYPCB […]
-
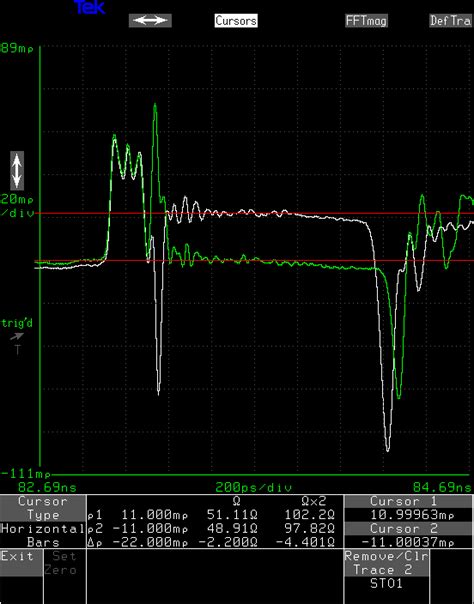 Read more: Differential trace impedance without reference plane
Read more: Differential trace impedance without reference planeWhat is Differential Trace Impedance? Differential trace impedance refers to the Characteristic Impedance of a differential pair of traces on a printed circuit board (PCB). A differential pair consists of two conductors that carry equal and opposite signals. The impedance of the pair is determined by the geometry and spacing […]
-
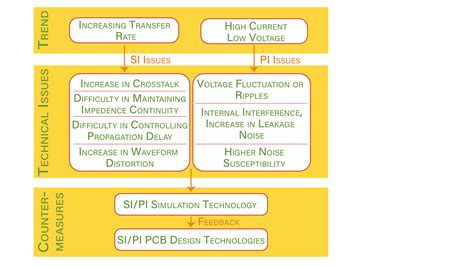 Read more: I O Optimization with 3D SoC SiP and PCB co design
Read more: I O Optimization with 3D SoC SiP and PCB co designIntroduction to SoC-PCB Co-Design In the rapidly evolving world of electronic design, the demand for high-performance, compact, and energy-efficient systems has never been greater. As the complexity of System-on-Chip (SoC) designs continues to increase, it becomes increasingly important to consider the interdependence between the SoC and the Printed Circuit Board […]
-
 Read more: PCB Layout Techniques to Achieve RF Immunity for Audio Amplifiers
Read more: PCB Layout Techniques to Achieve RF Immunity for Audio AmplifiersIntroduction Designing and laying out a printed circuit board (PCB) for an audio amplifier requires careful consideration of many factors to achieve optimal performance, reliability, and immunity to radio frequency (RF) interference. RF noise can couple into sensitive audio circuitry and cause distortion, hum, and other unwanted artifacts that degrade […]
-
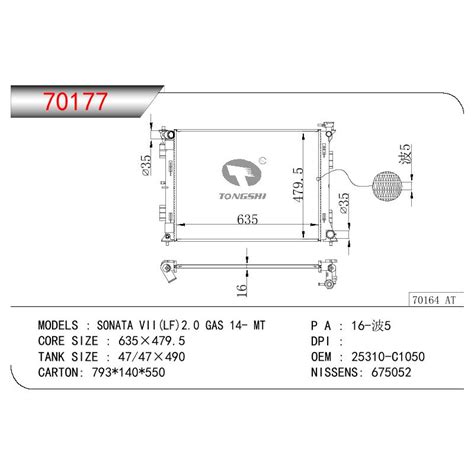 Read more: Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata central locking circuit diagram
Read more: Beijing Hyundai Sang Nata central locking circuit diagramIntroduction to Hyundai Nata Central Locking System The Hyundai Nata is a popular car model produced by Beijing Hyundai, a joint venture between Hyundai Motor Company and Beijing Automotive Industry Holding Co., Ltd. One of the essential features of the Nata is its central locking system, which allows the driver […]
-
Fly Buck converter PCB layout tips
Posted by
–
 Read more: Fly Buck converter PCB layout tips
Read more: Fly Buck converter PCB layout tipsUnderstanding the Fly Buck Converter Topology A fly buck converter, also known as a buck converter with synchronous rectification, is a type of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) that efficiently steps down a higher voltage to a lower voltage. The basic components of a fly buck converter include: High-side MOSFET (Q1) […]
Recent Posts
- Best Practices to Ensure the Correct Component Orientation by Optimized assembly PCB board!
- Build a New Product quickly with PCB Assembly Prototyping – A Brief Guide!
- Can you provide complete PCB box-build services?
- Tips for Choosing the Perfect Cable Assembly Manufacturer!
- Top 10 Best PCB routing practices!
Categories
- PCB Blog 835




